In this lesson we will learn how to install debian and docker and run your python scripts
Requirements
- Pfsense must be configured correctly and running - link ( Just follow till you have a working pfsense and skip the docker part)
Prerequisites
- Download the official debian full dvd iso - link
Installation
Debian
Make sure pfsense is running in the background
Start your debian machine and follow the instructions
Everything should work perfectly if you are following my guide.
Root privileges
su
# root password
sudo usermod -aG sudo your-username
exit
newgrp sudoUse Apt
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list Copy this into the file
deb https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
# deb-src https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
deb https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-updates contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
# deb-src https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-updates contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
deb https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-proposed-updates contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
# deb-src https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-proposed-updates contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
deb https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-backports contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
# deb-src https://ftp.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-backports contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
deb https://security.debian.org/debian-security/ bookworm-security contrib main non-free non-free-firmware
# deb-src https://security.debian.org/debian-security/ bookworm-security contrib main non-free non-free-firmwareContinue to docker installation
Docker
Before you install Docker Engine for the first time on a new host machine, you need to set up the Docker apt repository. Afterward, you can install and update Docker from the repository.
⭐ You can follow the official guide here for troubleshooting :
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/debian/
Video guide :
- Set up Docker's apt repository.
# Add Docker's official GPG key:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
# Add the repository to Apt sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get updateIf you use a derivative distro, such as Kali Linux, you may need to substitute the part of this command that's expected to print the version codename:
(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")Replace this part with the codename of the corresponding Debian release, such as bookworm.
- Install the Docker packages.
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin- Verify that the installation is successful by running the
hello-worldimage:
sudo docker run hello-worldThis command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints a confirmation message and exits.
You have now successfully installed and started Docker Engine.
Now we will create a docker group to run docker commands withouts sudo
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp dockerVerify that you can run docker commands without sudo.
docker run hello-worldConfiguration
We have now a working pfsense and a debian vm with docker installed. Now we will try to use pfsense to expose our python server to listen on the WAN IP so we can send requests to the server from any pc in the network.
Download the python scripts in your vm
Unzip the files and open the folder in terminal
You will have these files
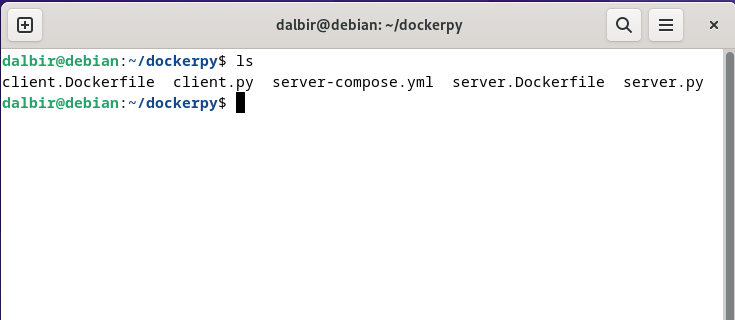
Docker containers
Now we will start by building the server with docker and exposing to our local network and use our client to connect to it
Server
docker build -f server.Dockerfile -t python-server .
docker compose -f server-compose.yml up -dClient
docker build -f client.Dockerfile -t python-client .
docker run -it --network s4_tcp python-client python-server 1234 "https://api.ipify.org"As we can see, our docker python-server is running and respond back to client requests by specifying the ip port and url which we want to get the response from. Now we will use our pfsense to expose this to the WAN IP and see if it still works
Pfsense
Make sure python-server is running in background
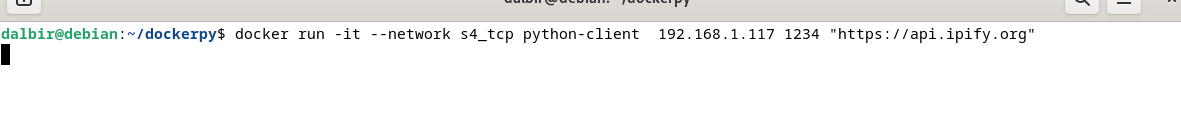
Currently running python-client by specifying WAN IP doesn't work we haven't exposed these ports to the public yet.
We will start by adding a new rule in pfsense to expose our debian vm IP and port
Firewall → NAT
Click on Add and use the following information
Change IP to your debian vm ip and enable NAT reflection with proxy
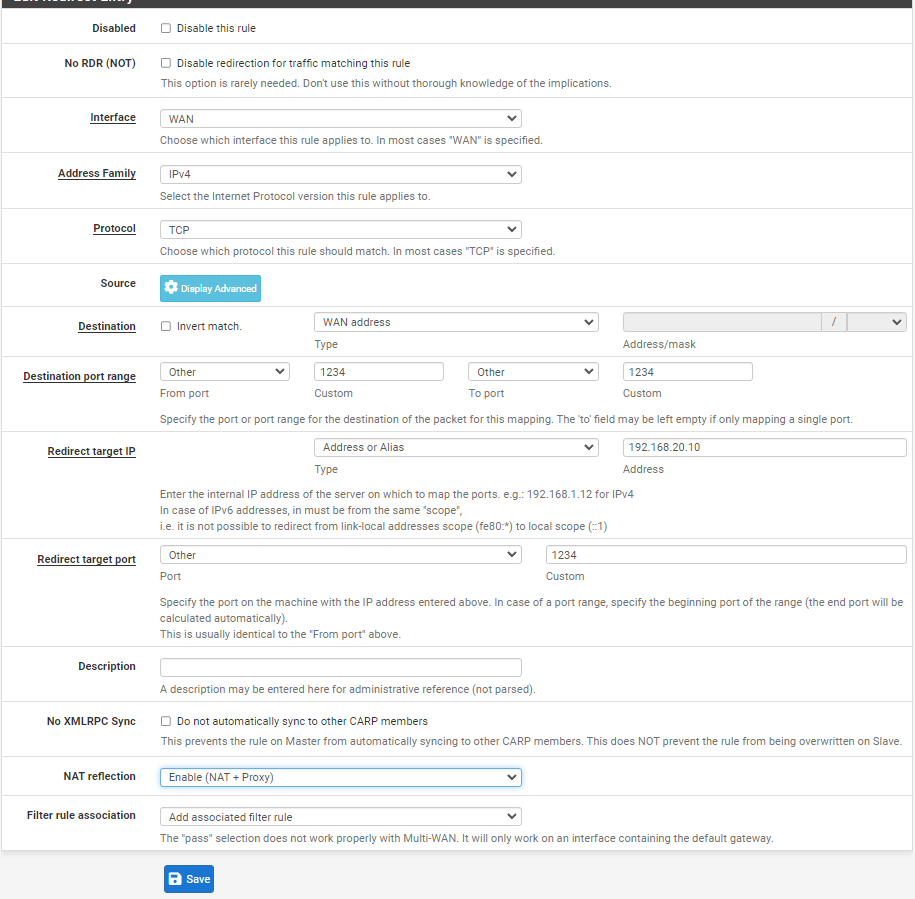
Save and Apply changes
Now we will try to connect to our python-server from pfsense WAN IP
docker run -it python-client WANIP 1234 "https://api.ipify.org"

And Voilà